Articulation
Connect models with articulated behavior using the articulation component
The articulation component provides a physical with the ability to be connected to other physical bodies with articulated constraints.
Properties
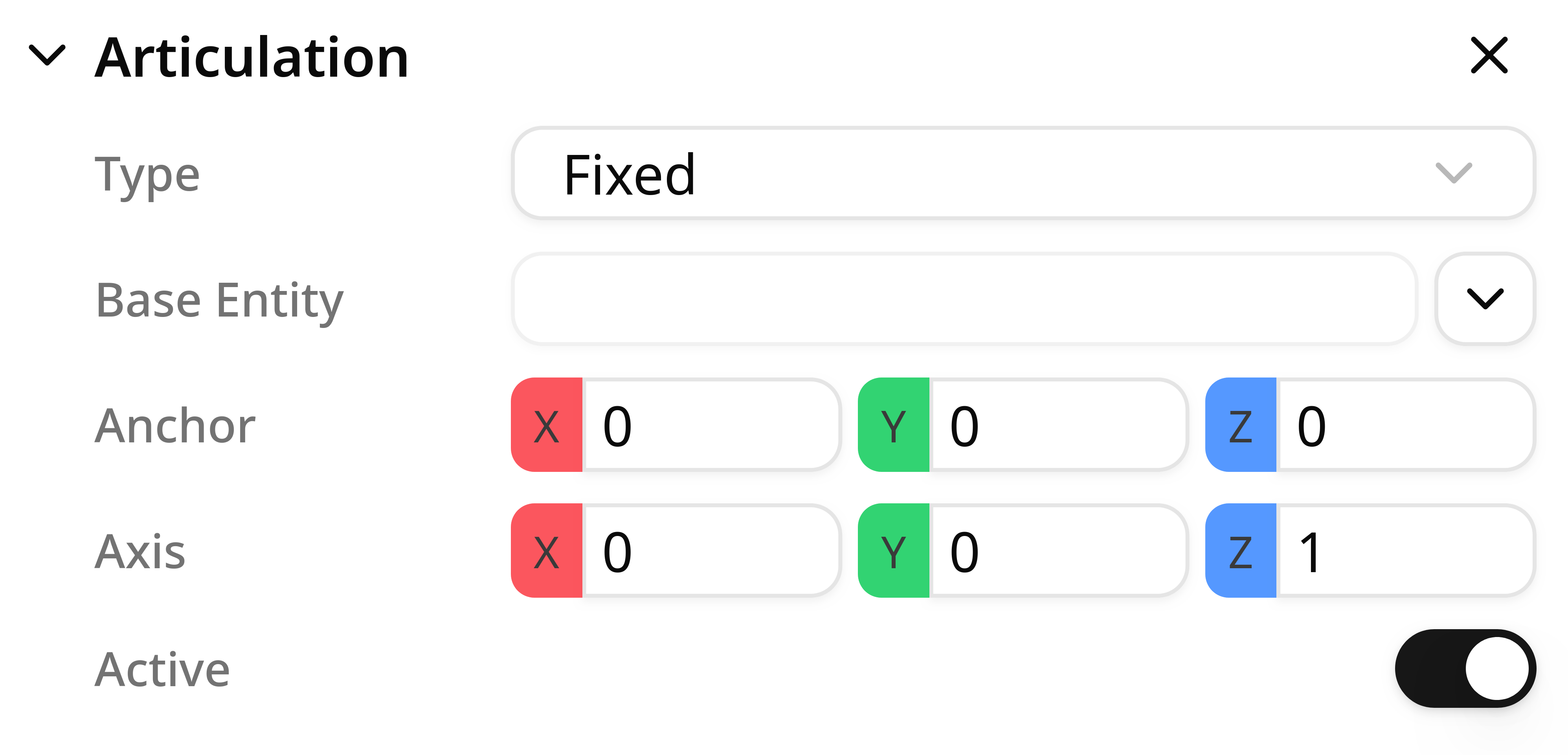
Type
The type of an articulation defines its behaviour in a kinematic chain. There are three supported types:
- Fixed: the articulation is fixed to the base entity.
- Revolute: the articulation rotates around a given axis, using a user-defined anchor as the joint reference.
- Prismatic: the articulation translates along a given axis, using a user-defined anchor as the joint reference.
A serial chain can mix articulation types freely, and can contain as many articulations as needed to match your design.
Base entity
Each kinematic chain is treated as a tree. To define the hierarchy correctly, you must set the base entity: the entity to which the current articulation is attached.
When selecting a base entity, the editor lists the objects that already have an Articulation component. Choose the one that the articulation you are creating should connect to.
Anchor
The anchor defines the base transform of the articulation you are creating (the joint reference frame).
- The anchor is defined in local space, meaning it is measured relative to the origin of the object where the articulation component is added.
Incorrect anchor setup
To prevent unwanted behaviours, be careful with your anchor placement. If the anchor is too far from the object's center of mass/center of actuation the articulation can turn unstable.
Axis
The axis defines the local direction along which movement occurs:
- Revolute: the articulation rotates around the axis.
- Prismatic: the articulation translates along the axis.
The axis is interpreted in the object's local coordinate space.
Tip
For predictable behaviour, make sure your object's local axes match the intended joint direction before setting the axis (for example by adjusting the object orientation in the Transform component).
Active
The active property controls whether the articulation has a motor attached or not.
If active, the articulation will be controllable through an Articulation Controller and Program Instructions. If not active, the articulation will follow the physics simulation without being controllable by the user.